Cyber-security is a topic I find fascinating but admit that my knowledge in the area is limited. Thankfully there are countless online resources available to help enthusiastic amateurs gain an understating of this complex world. One such resource that I became familiar with during the past year is LinkedIn Learning. Recently, I undertook a short course titled “Introduction to Ethical Hacking” by industry expert Lisa Bock. My rationale for undertaking this course was to gain a better understanding of a Penetration Testing service my company was offering to its clients. Thankfully the course didn’t get overly technical and was easy to follow and hugely interesting. One subject area that I found most interesting and something I had little or no knowledge of was the cyber kill chain. The kill chain will be explained in detail in this post but needless to say that given my lack of knowledge on the topic, the content of this post is taken from course learnings, online research and conversations with our own cyber experts.
Today’s Threat landscape
Today’s threat landscape is complex and continually evolving with current threats putting every business, government entity, and individual in the crosshairs. Malware is becoming more aggressive, and we are experiencing everything from network-based ransomware worms, to devastating wiper malware. Malicious actors are designing sophisticated malware that is polymorphic in nature meaning it can change or morph, making it more difficult to detect with antimalware programs. This behaviour makes it even more difficult to combat because the signatures are constantly changing. A significant percentage of global traffic is now encrypted; however, this can also be a double-edged sword. We know that encryption is employed to protect our data from prying eyes, but now malicious actors are also using encryption to conceal their activity when communicating with a command-and-control server and moving through your network in the form of an advanced persistent threat. Email continues to be the number one attack vector, and malicious actors are doubling down on using email and spam as an entry point to your systems and networks. They’re using specially crafted spear-phishing attacks that prey on our fears, such as using a current topical event to lure someone into opening an email and clicking on a link. The internet of things (IoT) is another attack vector to gain access with many IoT devices untested and with many vulnerabilities that can lead to a successful attack. With wave after wave of cyber-attacks on the horizon it’s now more important than ever to reduce your exposure to risks, by making strategic security improvements, and adhering to best practices to better defend your organisation.
Understanding the Cyber Kill Chain
An advanced persistent threat is when a malicious actor gains access to a network and remains undetected for weeks, months and even years. Lockheed developed the Cyber Kill Chain with the idea that if we identify threats early enough, this will reduce the possibility of an advanced persistent threat. The cyber kill chain is an adaptation of the military’s kill chain, a step-by-step approach that identifies and stops the enemy activity.
How does the Cyber Kill Chain Work?
The seven phases of the Cyber Kill Chain enhance visibility into an attack and enrich an analyst’s understanding of an adversary’s tactics, techniques and procedures. They are:
Phase 1: Reconnaissance
This is the observation stage where the attacker gathers information on their target and develops tactics for the attack. They can use automated scanners to find vulnerabilities they may be able to penetrate. They will try to identify a point of entry by investigating the security systems in place including firewalls, Endpoint Protections, and authentication mechanisms.
Phase 2. Weaponization
Once they have gathered enough information and identified a vulnerability or point of entry, they will start looking at the appropriate attack vectors to gain entry to your system or network. This could be as simple as using weak or stolen credentials or developing malware to exploit the identified vulnerabilities.
Phase 3: Delivery
This is the most crucial stage whereby the intruder launches the attack. The specific steps taken will depend on the type of attack they intend to carry out. For example, the attacker may send email attachments or a malicious link to spur user activity to advance the plan. This activity may be combined with social engineering techniques to increase the effectiveness of the campaign. The Cyber Awareness of the victim at this stage may well determine if an attack is successful, or not.
Phase 4: Exploitation
Now that the payload is on the network, the malicious actor’s set up to make their move by exploiting a vulnerability. They could exploit the following, missing input validation, lack of sufficient logging, not closing the database connection, or using obsolete or deprecated methods.
Phase 5: Installation
A backdoor or remote access trojan is installed by the malware that provides access to the intruder.
Phase 6: Command & Control
If a hacker sees the opportunity for future attacks, their next move is to install a backdoor for consistent access to the target’s systems. This way they can move in and out of the target’s network without running the risk of detection by re-entering through other attack vectors. Take the HSE attack here in Ireland for example. The attackers had access to their systems for 8 weeks before they launched the ransomware attack that crippled their systems.
Phase 7: Actions on Objectives
Intruder initiates end goal actions, such as data theft, data corruption, or data destruction.
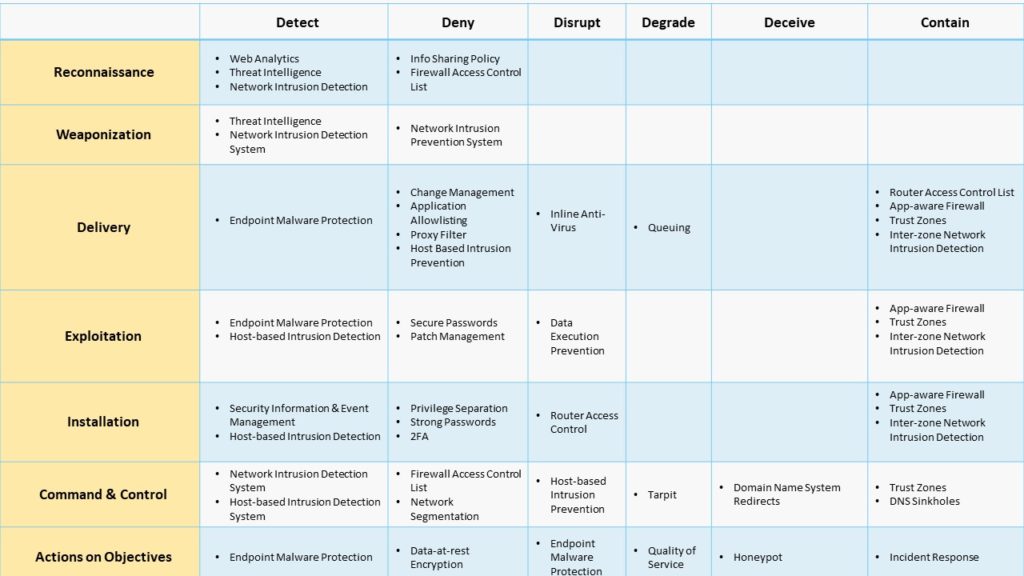
Security Controls to stop an attack in the Kill Chain
The following 6 methods an organization can use to stop an attack are proposed by SBS Security
- Detect – Determine attempts to scan or penetrate the organization.
- Deny – Stop attacks as they happen.
- Disrupt -Intercept data communications carried out by the attacker and interrupt them.
- Degrade – Create measures that will limit the effectiveness of an attack.
- Deceive – Mislead an attacker by providing false information or setting up decoy assets.
- Contain: Limit the scope of an attack to particular segments of your network or organisation.
The following information shows how security tools can be used to apply each of the security controls to each kill chain stage.
The kill Chain Isn’t Perfect
The Kill Chain by Lockheed Martin is a good framework in terms of helping you gain an understanding of the anatomy of a cyber-attack but if there’s one thing we’ve learned, it’s that malicious actors don’t follow any playbook and may skip steps or add new steps as they go about exploring new ways of infiltrating systems. Recent studies suggest that up to 88% of attacks now combine stages 1-5 into a single action. Also, not every attack falls under the Lockheed framework. For example, an attack featuring compromised credentials, whereby attackers gain access to systems with legitimate credentials wouldn’t fall under the framework. This is an ever-growing problem as we invest more and more in SaaS cloud services and the vast library of logins we have for the various services. Protecting your login credentials is now more important than ever as hackers don’t need to access your core networks to compromise your data. Getting access to a 3rd party service via your compromised credentials can be just as damaging as an attack on your own network.
Malicious actors wear many hats and maybe a single entity, a criminal organisation or state-sponsored but what is clear is that cyber-attacks are becoming more frequent and more sophisticated. Building multi-layered cyber defences will greatly mitigate the chances of a successful attack on your systems but with email still being the Number one threat vector, it’s the cyber awareness of your team that will prove to be your greatest cyber defence asset.














