The cyber security landscape is continually evolving; however, a good understanding of the current threats and preventative measures is a vital first step towards an effective defence. The inspiration for this post comes from this excellent animated illustration below, found on the LinkedIn page of The Cyber Security News. It succinctly outlines the top 8 types of cyber-attacks, a crucial piece of information for anyone keen on safeguarding their digital environments. For this post we expanded on the available information to further explain each type of threat, the methodology of the attack and preventive measures that should be taken to greatly mitigate against an attack. Here are the top eight types of cyber-attack presently in existence.
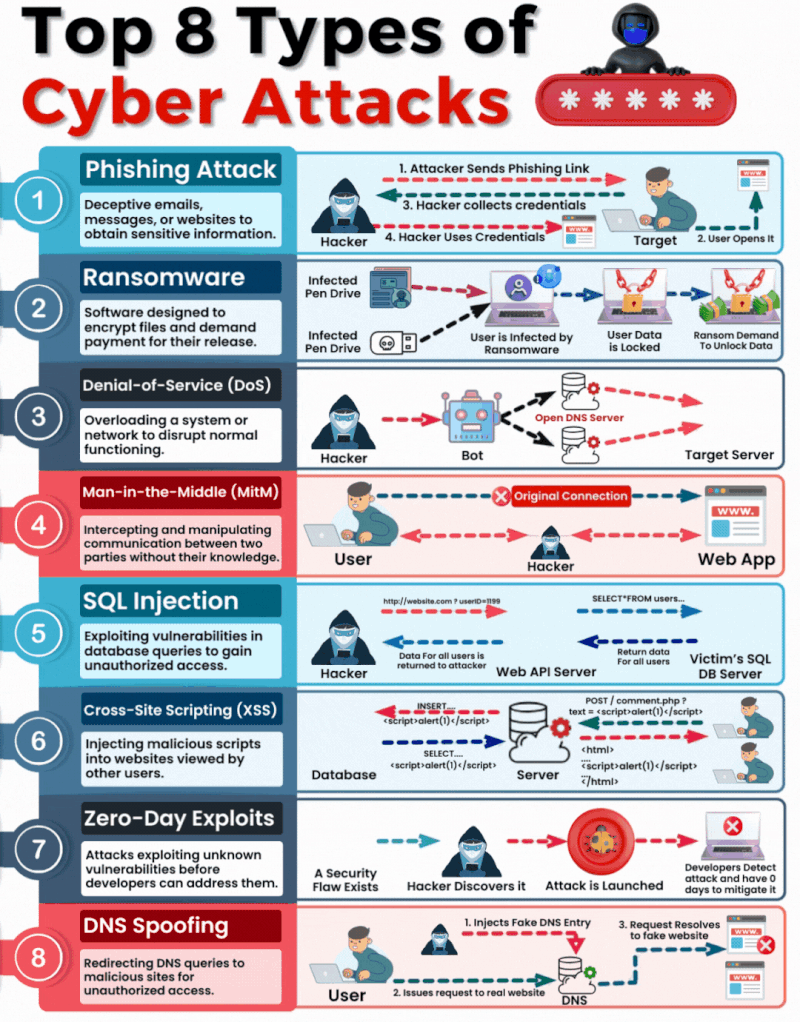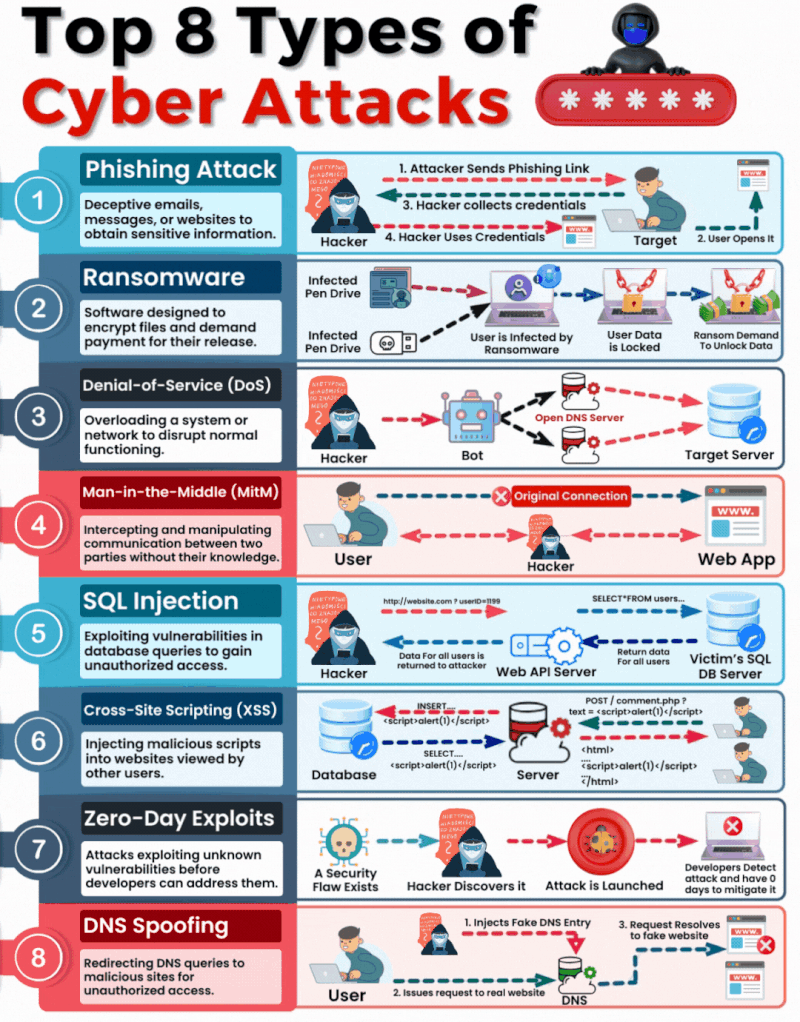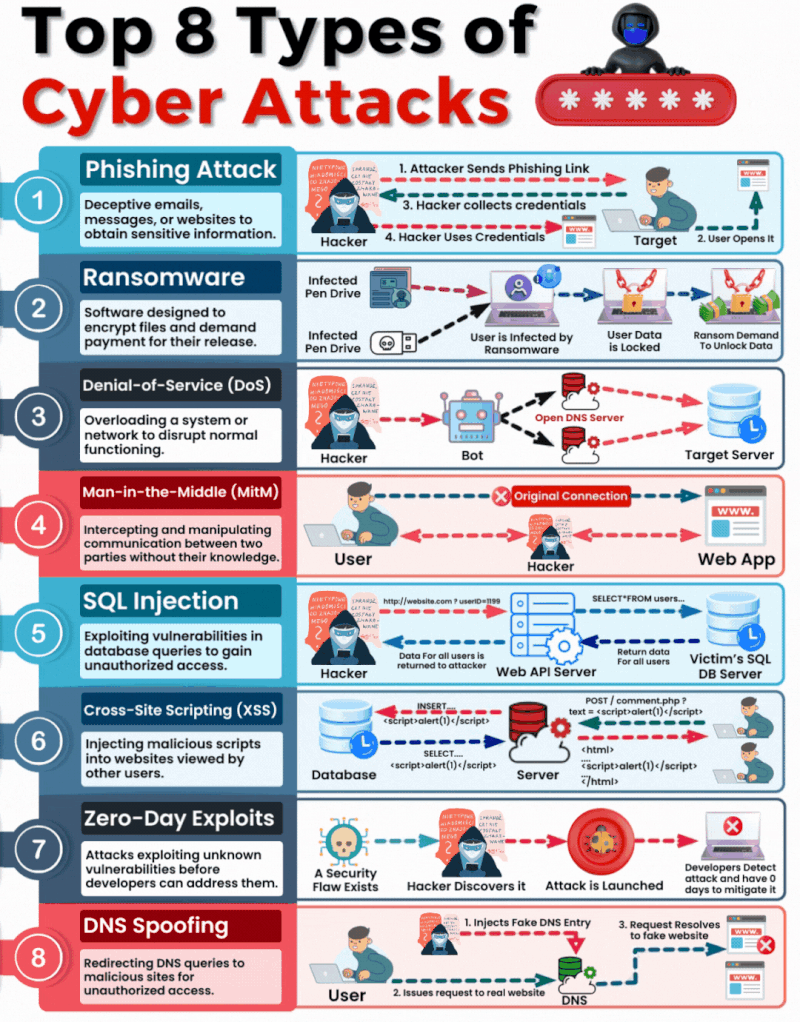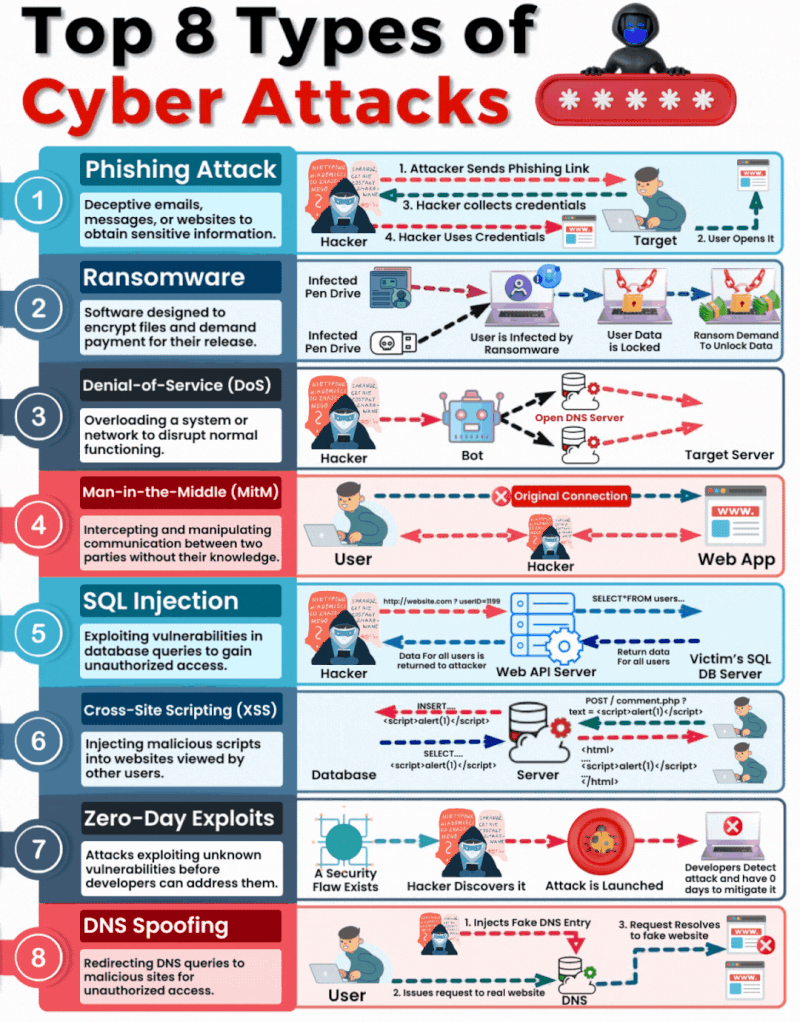
1. Phishing
What It Is & How It Operates: Phishing involves sending fraudulent communications that appear to come from a reputable source, usually through email. The goal is to steal sensitive data like credit card numbers and login information or to install malware on the victim’s machine.
How You Can Be Targeted: People are targeted through seemingly legitimate emails or messages that urge the recipient to take an action such as clicking on a link or downloading an attachment. Common lures include urgent requests for information, offers of refunds, fake alerts, or required security checks.
Prevention Measures:
- Always verify the sender’s email address for authenticity.
- Avoid clicking on links or downloading attachments from unknown or suspicious sources.
- Implement advanced spam filters and security protocols.
- Educate employees and individuals on recognising phishing attempts.
2. Ransomware
What It Is & How It Operates: Ransomware is a type of malicious software that encrypts a victim’s files, with the attacker demanding a ransom to restore access. Initially, these attacks simply locked access to data, but modern variants often threaten to release the encrypted data publicly on the dark web if the ransom is not paid, significantly raising the stakes.
How You Can Be Targeted: Victims can download ransomware from a malicious website or email attachment. It can also spread across networks by exploiting security vulnerabilities, often without any user interaction. Increasingly, attackers are targeting organisations with sensitive data, where the repercussions of public data exposure are more severe.
Prevention Measures:
- Keep all software up to date to patch vulnerabilities that could be exploited.
- Back up data regularly to secure and separate locations, ensuring that backups are not accessible for modification from the systems where the data resides.
- Employ robust antivirus software and firewalls to detect and block ransomware.
- Train staff to recognise the signs of phishing attempts and suspicious emails, as these are common vectors for ransomware attacks.
- Implement network segmentation to limit the spread of ransomware if an attack occurs.
- Regularly conduct security audits and vulnerability assessments to strengthen your cyber defences.
3. Denial-of-Service (DoS)
What It Is & How It Operates: DoS attacks flood servers, systems, or networks with traffic to exhaust resources and bandwidth. This overwhelms the system, making it slow or completely unresponsive to legitimate traffic.
How You Can Be Targeted: Targets are typically websites or services provided by the victim. Attackers might use compromised computers as part of a botnet to magnify the attack’s impact.
Prevention Measures:
- Invest in high-quality network hardware that can handle abnormal traffic spikes.
- Configure network architecture to disperse loads uniformly.
- Partner with ISPs that offer DoS mitigation.
- Use cloud-based DoS protection services that can absorb and reroute malicious traffic.
4. Man in the Middle (MitM)
What It Is & How It Operates: MitM attacks involve intercepting and potentially altering the communication between two parties without their knowledge. This can occur in any form of online communication, such as banking, email, or social networking.
How You Can Be Targeted: Attackers might eavesdrop on unsecured public Wi-Fi networks or compromise network devices using malware to intercept data transmitted over the network.
Prevention Measures:
- Always use HTTPS for secure communication.
- Avoid conducting sensitive transactions over public or unsecured Wi-Fi networks.
- Employ VPN solutions for encrypted communications.
- Regularly update and secure network equipment.
5. SQL Injection
What It Is & How It Operates: SQL injection involves inserting malicious SQL code into databases via web page input mechanisms, exploiting vulnerabilities to manipulate or steal data.
How You Can Be Targeted: Websites that do not properly sanitise inputs given by the user are susceptible. Attackers can input malicious SQL into these fields to manipulate the database.
Prevention Measures:
- Use prepared statements and parameterised queries to prevent SQL injection.
- Regularly update and patch database management systems.
- Conduct regular security audits of website and database.
6. Cross-site Scripting (XSS)
What It Is & How It Operates: XSS attacks involve injecting malicious scripts into web pages viewed by other users, which execute when loaded in the user’s browser. This can result in unauthorised access to cookies, session tokens, or other sensitive information retained by the browser.
How You Can Be Targeted: Users are targeted by visiting websites where XSS malicious scripts have been injected.
Prevention Measures:
- Employ Content Security Policy (CSP) headers to prevent XSS.
- Sanitise all user inputs to ensure they do not contain executable content.
- Use frameworks and libraries that automatically handle XSS prevention.
7. Zero-Day Exploits
What It Is & How It Operates: Zero-day exploits target unknown vulnerabilities in software or hardware, which have not yet been patched. They can lead to unexpected attacks and are particularly dangerous because there is no known defence when they are first exploited.
How You Can Be Targeted: Zero-day exploits are typically used in targeted attacks against specific organizations or broad attacks against popular software before the general public is aware.
Prevention Measures:
- Implement advanced threat detection systems.
- Keep all systems and software updated.
- Use security solutions with heuristic and behavioural analysis capabilities.
8. DNS Spoofing
What It Is & How It Operates: DNS Spoofing involves altering DNS records to redirect a website’s traffic to a fraudulent site without the user’s knowledge. This can be used to collect personal information, spread malware, or commit other acts of fraud.
How You Can Be Targeted: Users are targeted by accessing manipulated DNS records which lead them to malicious sites pretending to be legitimate ones.
Prevention Measures:
- Use DNSSEC (Domain Name System Security Extensions) for verifying DNS responses.
- Regularly monitor and audit DNS records.
- Ensure secure network configurations to avoid vulnerabilities that could be exploited in DNS spoofing attacks.
The cyber threats outlined above represent some of the most critical challenges facing businesses today. Understanding these threats is the first step towards defending against them. At IT.ie, we are dedicated to providing state-of-the-art cybersecurity solutions that protect Irish businesses from these sophisticated cyber-attacks. Our team is here to ensure your business is prepared and resilient against any cyber threat.
Contact IT.ie today for comprehensive cyber protection strategies and services that keep you one step ahead in cybersecurity.














